Kendrion is your expert for brakes
in various robotic applications
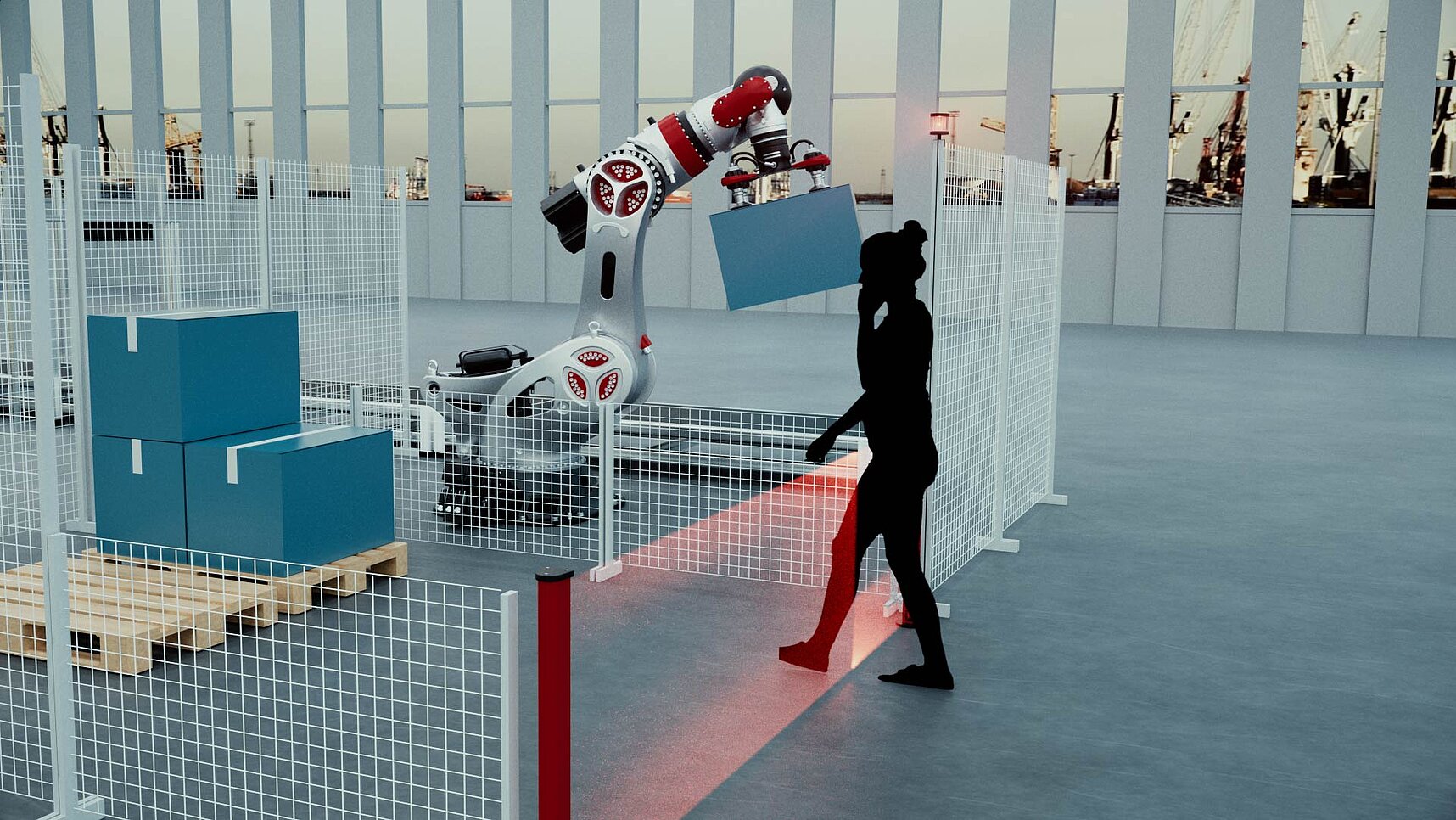
The robot market is growing. The wide range of models is constantly expanding the range of applications, and in the meantime, even smaller companies can automate their operations and make production processes more economical with the help of articulated arm robots, lightweight robots or cobots (collaborative robots). However, with both large and small robots, safety is the top priority. To ensure that neither humans nor capital goods are damaged in the event of a control or power failure, electromagnetic brakes are installed in the axes to hold the robot arm safely in position in the event of a malfunction. Different functional principles, sizes and performance classes ensure that the right brakes can be found for the various robots.
Different installation conditions
However, the installation conditions for safety brakes differ, depending on the type of robot. With large industrial robots, the brakes can usually be easily accommodated; there is sufficient space on the externally mounted servo motors. Things become more difficult in the rapidly growing market for small articulated arms, Scara and collaborative robots. Here, the motors are often located directly in the joint without housing, in which the safety brake must also find its place.
Choosing the right brake
Our broad product portfolio of holding brakes for robotics contains suitable solutions for every application: permanent magnet brakes for industrial robots that offer particularly high torques in a small installation space, small brakes for grippers that reliably hold the workpiece, or flat brakes with a very large inner diameter to route the cables.
Where standard solutions are out of the question, Kendrion offers the user the right solution - tailored to the individual application.
Our Heroes for robotic solutions
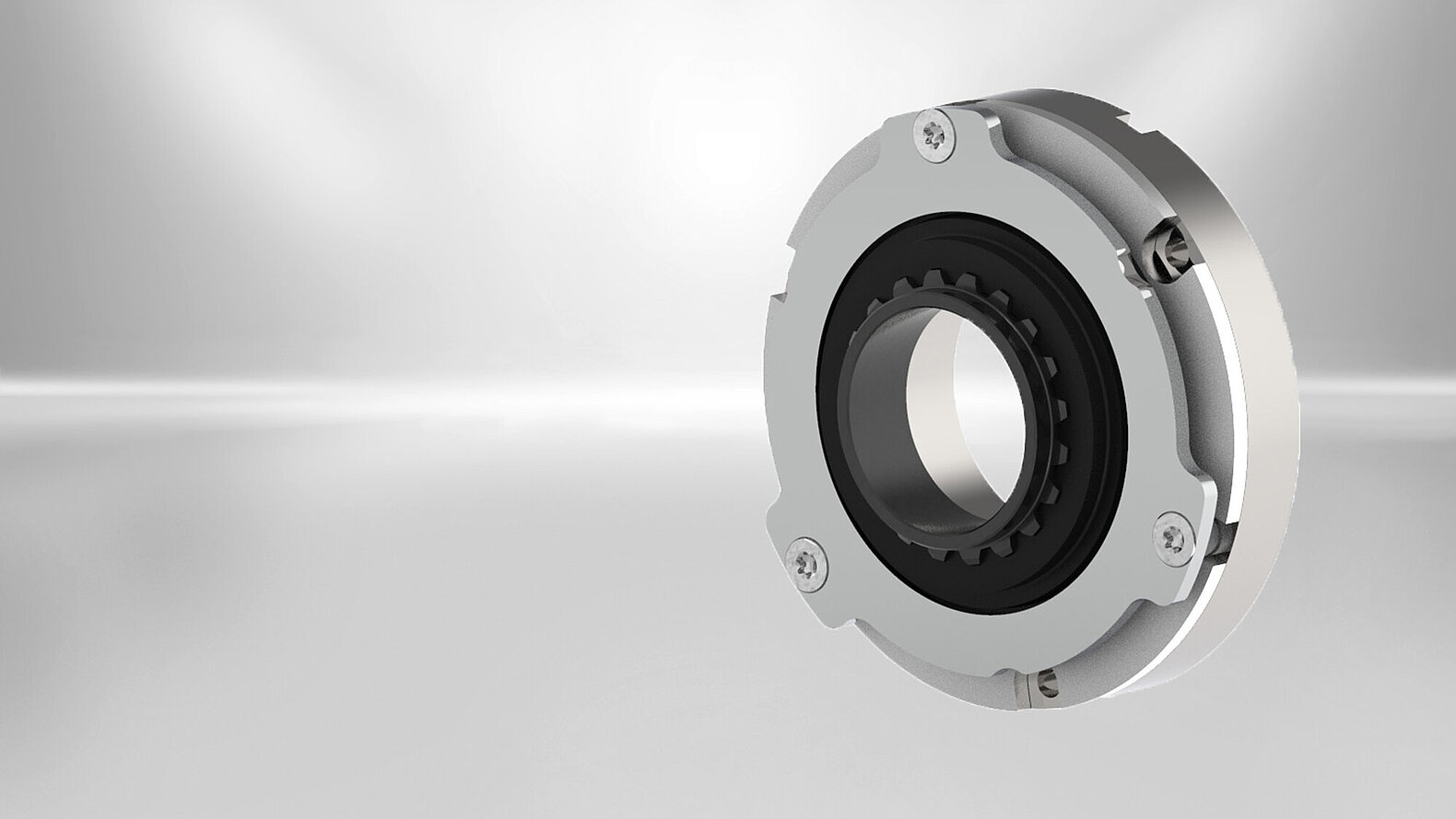
Spring-applied brakes Servo Slim Line
Electromagnetically actuated brakes are designed to bring a moving load to a standstill and hold it or to fix the position of an inactive load. The closing or opening of the brake usually must happen in a split of a second to be able to brake loads quickly and safely in high-frequency applications.
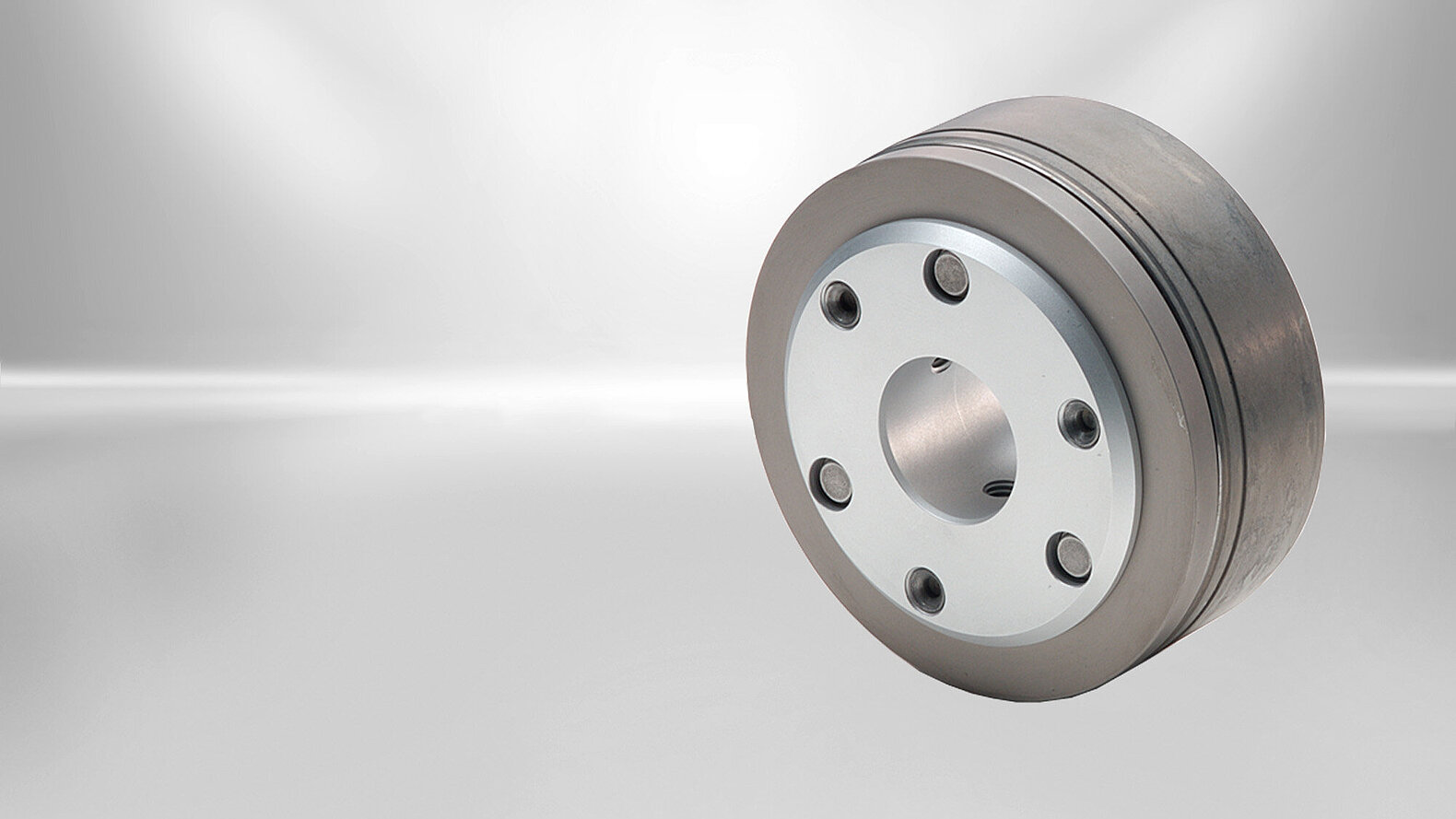
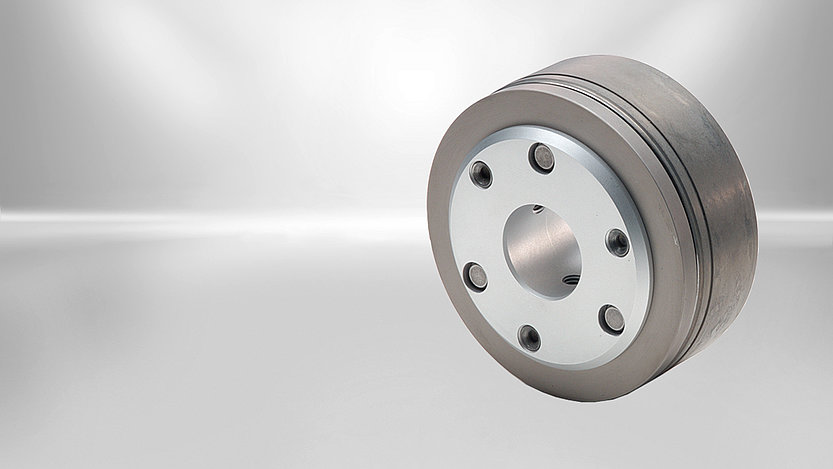
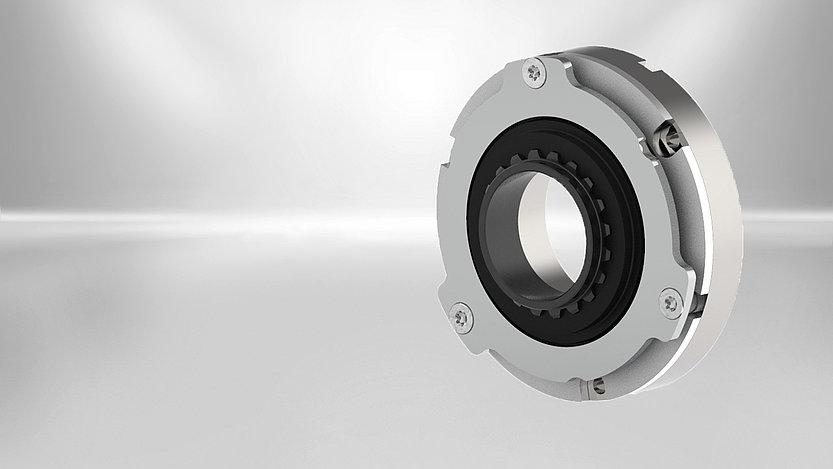
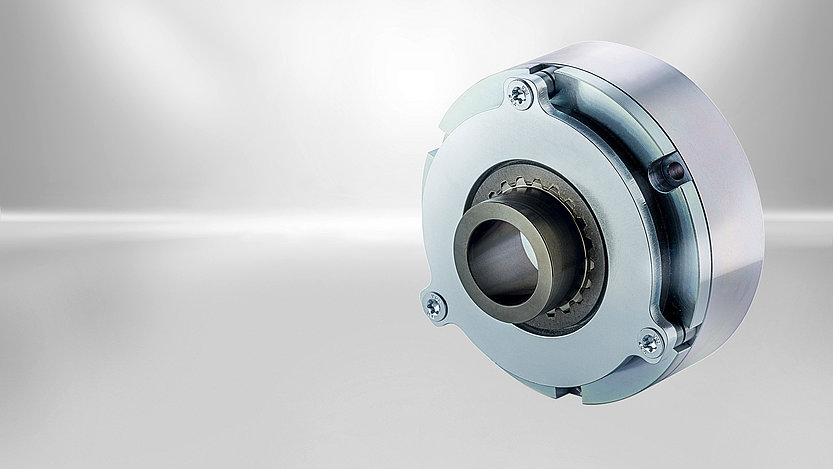
The Servo Slim Line spring-applied brake was designed primarily for applications with hollow shafts and small installation spaces. The "slim" single-disc brakes are flatter and lighter than the market standard in relation to their power density. Their large inner diameter makes them perfect for hollow shaft drives where the cables are routed inside through the joint or for applications where only minimal installation space is available.
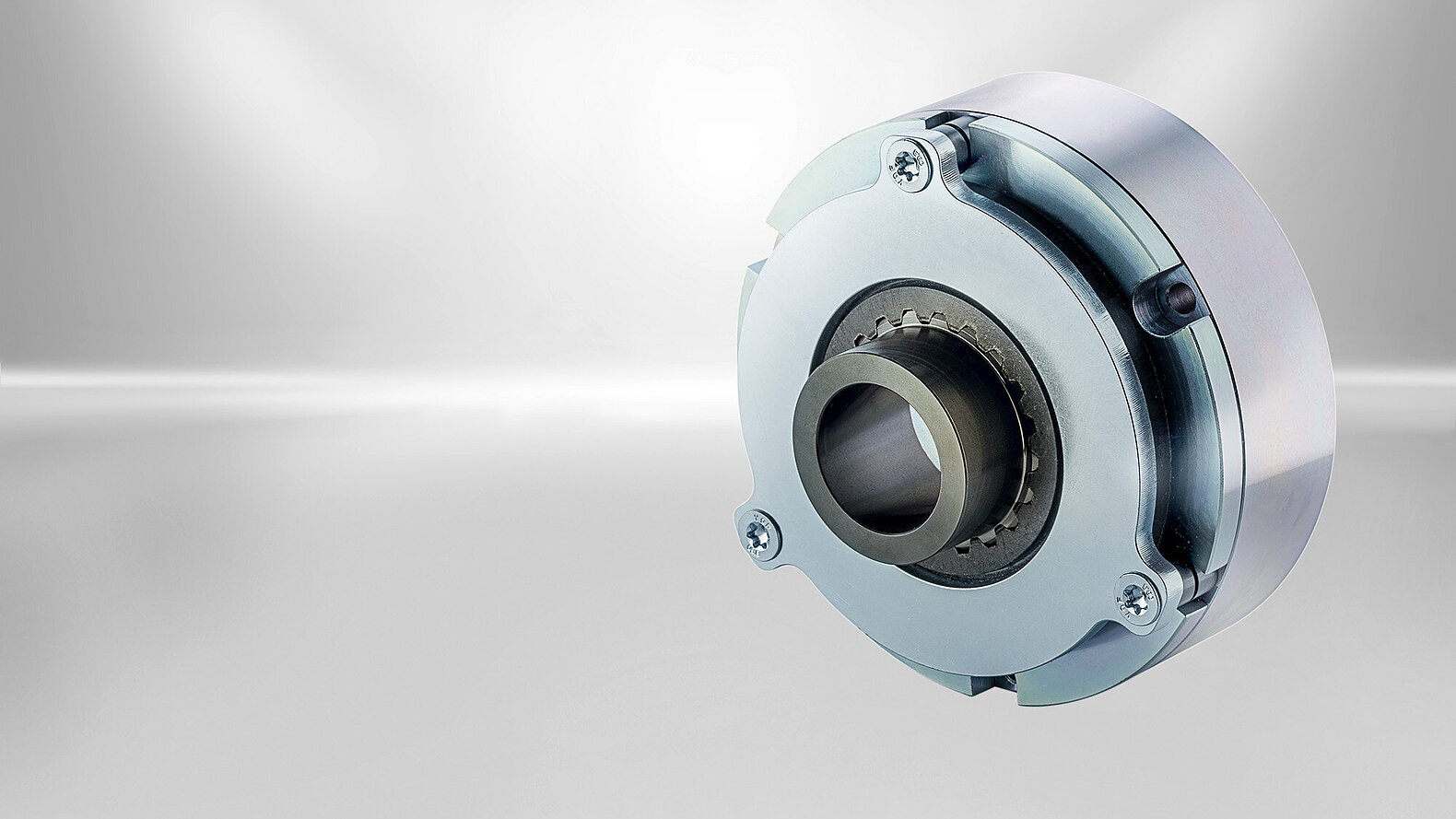
Permanent magnet brakes High Torque Line
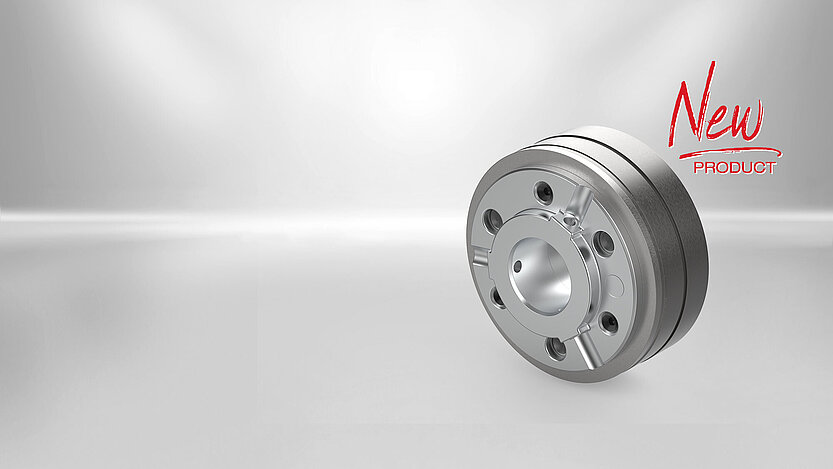
There are more and more new motor series on the market that deliver higher torques and require stronger brakes in the same installation space. "High Torque" permanent magnet brakes meet these high requirements. The basis is provided by a completely new design of the magnetic circuit and an optimized position of the pole surfaces.
The High Torque Line is available in different versions with torques from 0.1 to 280 Nm. They are easy to mount and very robust. Different armature designs are available as an option.
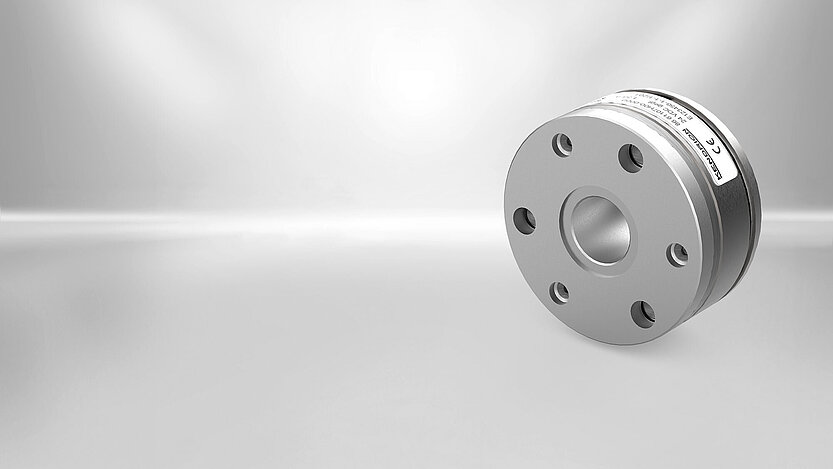
Spring-applied brakes Servo Line
Electromagnetically actuated brakes are designed to bring a moving load to a standstill and hold it or to fix the position of an inactive load. The closing or opening of the brake usually must happen in a split of a second to be able to brake loads quickly and safely in high-frequency applications.
The Servo Line spring-applied brake was designed primarily for applications with hollow shafts and small installation spaces. The "slim" single-disc brakes are flatter and lighter than the market standard in relation to their power density. Their large inner diameter makes them perfect for hollow shaft drives where the cables are routed inside through the joint or for applications where only minimal installation space is available.
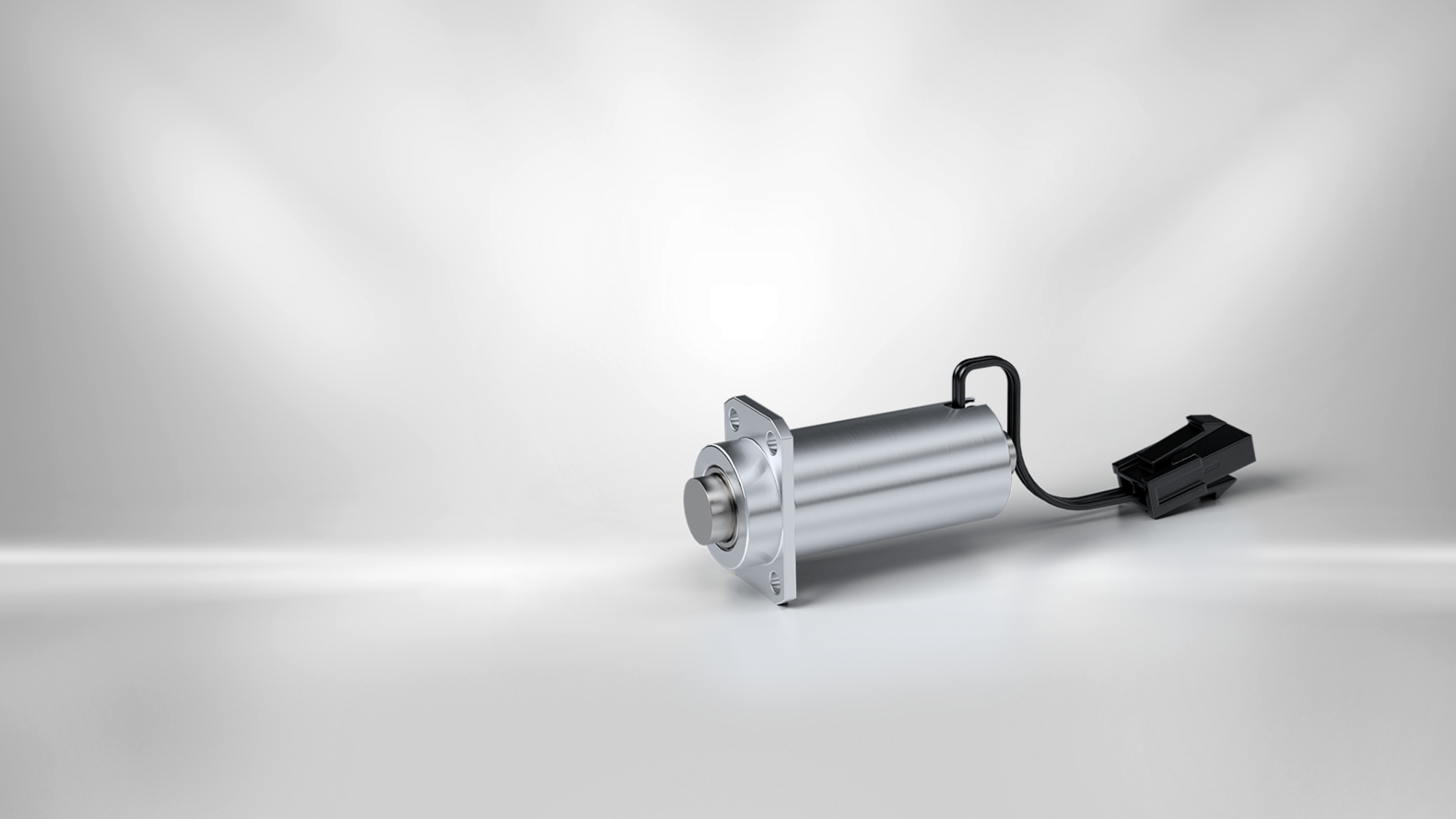

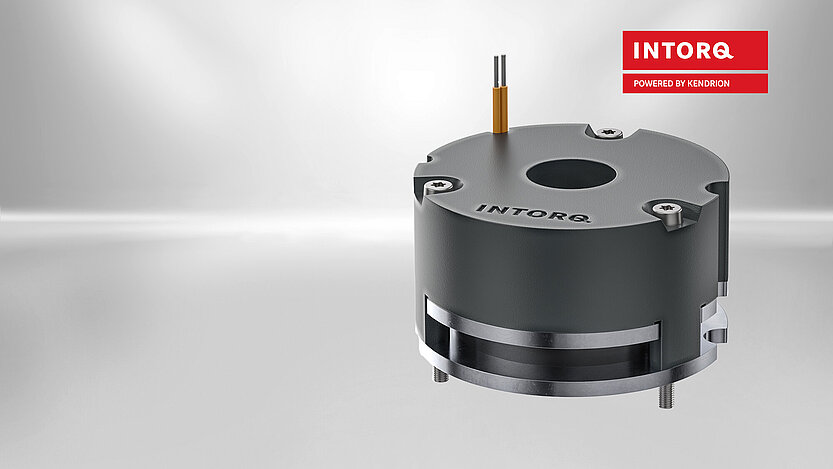
Robotic Joint Locking for Cobots
with the Emergency Solenoid Arrestor
Benefits at a glance
compact design
high safety due to currentless braking
low energy consumption due to overexcitation
high lateral force carrying capacity